![[ Deutsch ]](../../images/GERM001.gif) U-Value Calculator
U-Value Calculator
The U-Value Calculator is used for rapid calculation of U-Values for layered constructs.
Data of the layered structure can be saved into a layered construct file (<name>.LayeredConstruct).
Data can also be loaded from material layers file (<name>.MaterialLayers) or layered construct file (<name>.LayeredConstruct).
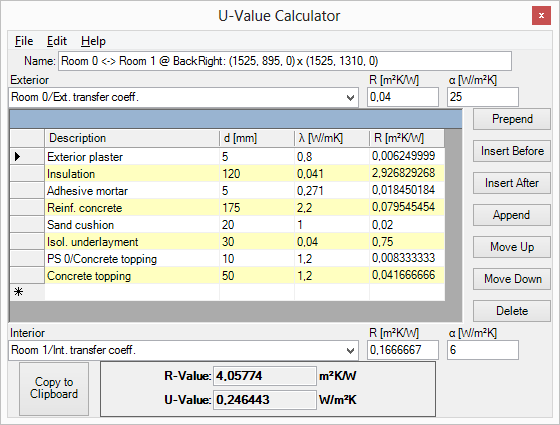
A layered construct contains a list of material layers surrounded by two surface (exterior and interior) boundaries.
For the two surface boundaries one can enter its surface heat transfer coefficient or transfer resistance. The Menu Edit→Surface transfer coeffs provides a choice of normative standard values. Both name fields of exterior and interior surfaces also provide same choices of standard normative values:
Material layers are input by the entry of their heat conductance and layer's thickness. Based on this values the program calculates heat resistance for each material layer.
The reciprocal value of the sum of resistances of all material layers and both surface transfers are displayed in the U-Value field.
Actually selected data line is marked by an arrow symbol at its left (data record mark). Multiple selection is also possible (e.g. for deletion of line which can be initiated with DEL key).
The complete layered construct can be placed onto the clipboard by the menu function Edit→Copy to be pasted later.
Tool specific control elements
| Insert | Inserts a new layer at the top of material layers list |
| Insert Before | Inserts a new layer before the one currently selected |
| Insert After | Inserts a new layer after the one currently selected |
| Append | Appends a new layer at the bottom of material layers list |
| Move Up | Moves the selected data line one position towards top of material layers list |
| Move Down | Moves the selected data line one position towards bottom of material layers list |
| Delete | Deletes the currently selected data line from material layers list Tip: To delete data line selected press the DEL key Remark: Pressing DEL key will delete all selected lines |
| Copy to Clipboard | A copy of current layered construct (all layers and the result) are placed onto the clipboard. Data placed onto the clipboard are are available there in different formats:
See also: Menu Edit→Paste, Edit→Copy |
Even if the order of layers and the inside/outside orientation do not matter for the calculation of the U-Value one can reorder layers within this tool as needed.
Tool specific menus
Menu items specific to this tool are presented in the main menu of the application:
| File→New | Creates a new, empty, structure of a layered construct. Warning: Save data prior to requesting this function! |
| File→Open... | Allows loading data of material layers (<name>.MaterialLayers) or layered construct (<name>.LayeredConstruct) from a file. Warning: Save data prior to requesting this function! |
| File→Save... | Allows storing the data of a layered construct into separate file (<name>.LayeredConstruct). |
| File→Exit | Closes the U-Value calculator window Warning: Save data prior to requesting this function! |
| Edit→Copy | A copy of current layered construct (all layers and the result) are placed onto the clipboard. Data placed onto the clipboard are are available there in different formats:
Tip: To copy the resulting U-Value to the clipboard alone use the context menu f the respective result field (you reach this menu by pressing the right mouse button over the field). |
| Edit→Paste | The construct currently on the clipboard can be pasted (inserted) into the current one. |
|
Edit→ Surface transfer coeffs→... |
Provides a choice of normative standard values of surface transfer coefficients designed for interior and exterior surfaces. The list offers standard value pairs from EN ISO 6946:1996 and EN ISO 13788:2002. |
Standardised surface heat transfer coefficients
| Description | RSi [m²K/W] |
RSe [m²K/W] |
|---|---|---|
| Calculating heat losses due to transmission (by component and heat flow direction): | ||
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Exterior wall (not ventilated) | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Exterior wall, ventilated | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Partition wall | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Wall to unconditioned (cellar) | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Wall to uncond. garret | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Wall connected to ground | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Roof (not ventilated) - HS up | 0.10 | 0.04 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Floor to exterior (not ventilated) - HS down (passage; projecting component) | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Roof, ventilated - HS up | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Floor to exterior, ventilated - HS down (passage; projecting component) | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Intermediate ceiling (betw. cond. spaces) | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Floor to unconditioned (cellar) - HS down | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Ceiling to uncond. garret - HS up | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| EN ISO 6946:1996 Slab at ground | 0.17 | 0.00 |
| Calculating heat losses due to transmission through transparent components (windows): | ||
| EN ISO 10077:2003 Window vertical ±30° (planar surface)- HS hor. ±30° | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| EN ISO 10077:2003 Window horizontal 0°-60° (planar surface)- HS vert. ±60° | 0.10 | 0.04 |
| EN ISO 10077:2003 Window red. radiation/conv. (corners and butt joints) - HS hor. | 0.20 | 0.04 |
| Assessing the Mould and Condensation Risk (by component type): | ||
| EN ISO 13788:2001 Walls and slabs etc. (assessing mould and condensation risk) | 0.25 | 0.04 |
| EN ISO 13788:2001 Window panes and frames (assessing mould and condensation risk) | 0.13 | 0.04 |